React | 2020-07-29 23:02:14 361次 0次
进入 reconcileChildren 之前,先继续分析 updateClassComponent 内部的细节,主要是执行 processUpdateQueue 和生命周期的调用,最终进入调和过程。
一、类组件初次渲染
初次渲染过程如果还没创建实例,初始化生成实例 instance,然后挂载实例更新 instance.state,并且执行一些生命周期。
constructClassInstance 方法创建组件实例并返回:
// 接受三个参数 workInProgress, Component, nextProps(pendingProps)
function constructClassInstance(){
...
// 这里第二个参数是 context 但是没有这么用过
const instance = new ctor(props, context);
//初始化 state 挂载到 memoizedState
const state = (workInProgress.memoizedState =
instance.state !== null && instance.state !== undefined
? instance.state
: null);
// 将实例挂载到 workInProgress的stateNode 上
//同时将 instance._reactInternalInstance赋值workInProgress,可以通过实例找到 wip
// classComponentUpdater挂载到 instance.updater
adoptClassInstance(workInProgress, instance);
...
return instance;
}其中通过 adoptClassInstance 方法,给 instance.updater 挂载了 classComponentUpdater,这样通过 setState 调用时会触发 this.updater.enqueueSetState 开始调度更新,如下图所示:
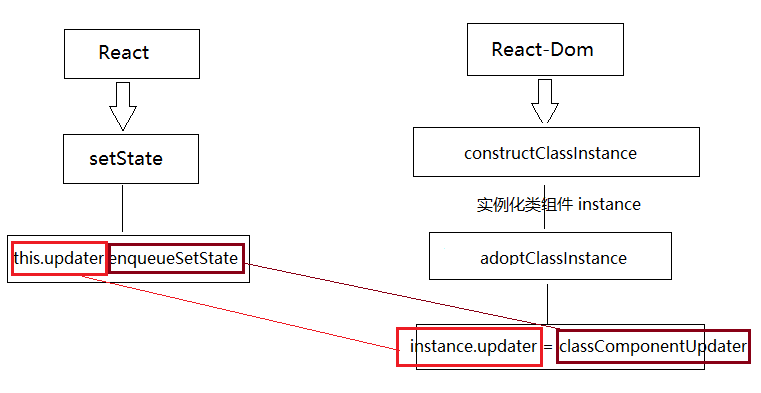
大致原理:
function Component(updater){
this.updater = updater || null
}
Component.prototype.setState = function() {
console.log(this.updater)
}
class Per extends Component{
inner = () => {
this.setState()
}
}
let s = new Per(11)
s.updater = '这里有一些方法'
s.inner() // 这里有一些方法mountClassInstance 生命周期钩子调用:
function mountClassInstance(): void {
...
//初始化一个更新队列
initializeUpdateQueue(workInProgress);
...
//遍历更新队列 计算state
processUpdateQueue(workInProgress, newProps, instance, renderExpirationTime);
//新的state上一步中被挂载到了 memoizedState 这里再赋值给实例的state
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState;
//getDerivedStateFromProps 新的生命周期 静态方法
const getDerivedStateFromProps = ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps;
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
applyDerivedStateFromProps(...);
//获取最新的state
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
// ComponentWillMount 钩子调用
if (...) {
// 这里面如果state发生变化会执行 enqueueReplaceState方法
callComponentWillMount(workInProgress, instance);
//执行更新队列 获取state
processUpdateQueue(...);
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
// componentDidMount 先打上标记
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Update;
}
}export function applyDerivedStateFromProps(
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any,
getDerivedStateFromProps: (props: any, state: any) => any,
nextProps: any,
) {
const prevState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
// 需要更新则返回一个对象,否则就是null
const partialState = getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState);
// 根据开发者返回的结果进行处理 数据不可变原则赋值
const memoizedState =
partialState === null || partialState === undefined
? prevState
: Object.assign({}, prevState, partialState);
workInProgress.memoizedState = memoizedState;
//更新队列
if (workInProgress.expirationTime === NoWork) {
// Queue is always non-null for classes
const updateQueue: UpdateQueue<any> = (workInProgress.updateQueue: any);
updateQueue.baseState = memoizedState;
}
}初始渲染是 shouldUpdate 标记为 true,因为第一次必须要执行更新。
二、被中断的继续执行
进入第二个分支中的判断,实例存在,但是 current 不存在,意味着被中断过需要再次执行,此时直接复用创建的实例即可。
function resumeMountClassInstance(): boolean {
...
// getDerivedStateFromProps如果存在,则不执行callComponentWillReceiveProps
// 这个方法是不安全的 因为这里可能会被执行多次
if (
!hasNewLifecycles &&
(typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps === 'function' ||
typeof instance.componentWillReceiveProps === 'function')
) {
if (oldProps !== newProps || oldContext !== nextContext) {
callComponentWillReceiveProps(...);
}
}
...
if (...) {
//组件不需要更新 终止
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Update;
}
return false;
}
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
//getDerivedStateFromProps 调用 同第一部分
}
const shouldUpdate = checkShouldComponentUpdate(...);
if (shouldUpdate) {
if (
!hasNewLifecycles &&
(typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount === 'function' ||
typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function')
) {
// getDerivedStateFromProps如果存在,则不执行 componentWillMount
}
// cDM 标记
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Update;
}
} else {
// 组件不需要更新
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Update;
}
// 这里尽管不需要更新 为了后面节点复用 依赖双缓冲 插眼
workInProgress.memoizedProps = newProps;
workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;
}
...
return shouldUpdate;
}这个方法会返回是否更新的标识,这里面去做钩子调用时候会加入 getDSFP 存在判断,存在就不使用旧的钩子。componentWillReceiveProps 方法所谓的不安全可以从两点考虑:
① oldProps !== newProps因为引用不同,所以这个条件永远成立,只要父组件发生变化,子组件这个方法一定会执行,开发不当会造成无限循环
② 当前架构模式下这个方法有可能会被执行多次,和旧版本中的表现形式不一致(只会执行一次)
其中 ShouldComponentUpdate 中先根据开发者返回的结果执行,还会进行 pureCom 的判断,就是默认给加一层 shallowEqual 浅比较,这些方法都很简单。
需要注意的是尽管不需要更新的情况,仍然记录了新的属性和状态,是为了后面复用节点。
三、更新渲染
updateClassInstance 更新渲染,到这里贴两张 react 的生命周期图(原有钩子和新增钩子),这个方法就不贴代码了,里面就是这些钩子的调用以及 state 的计算。(图是亲手盗的)
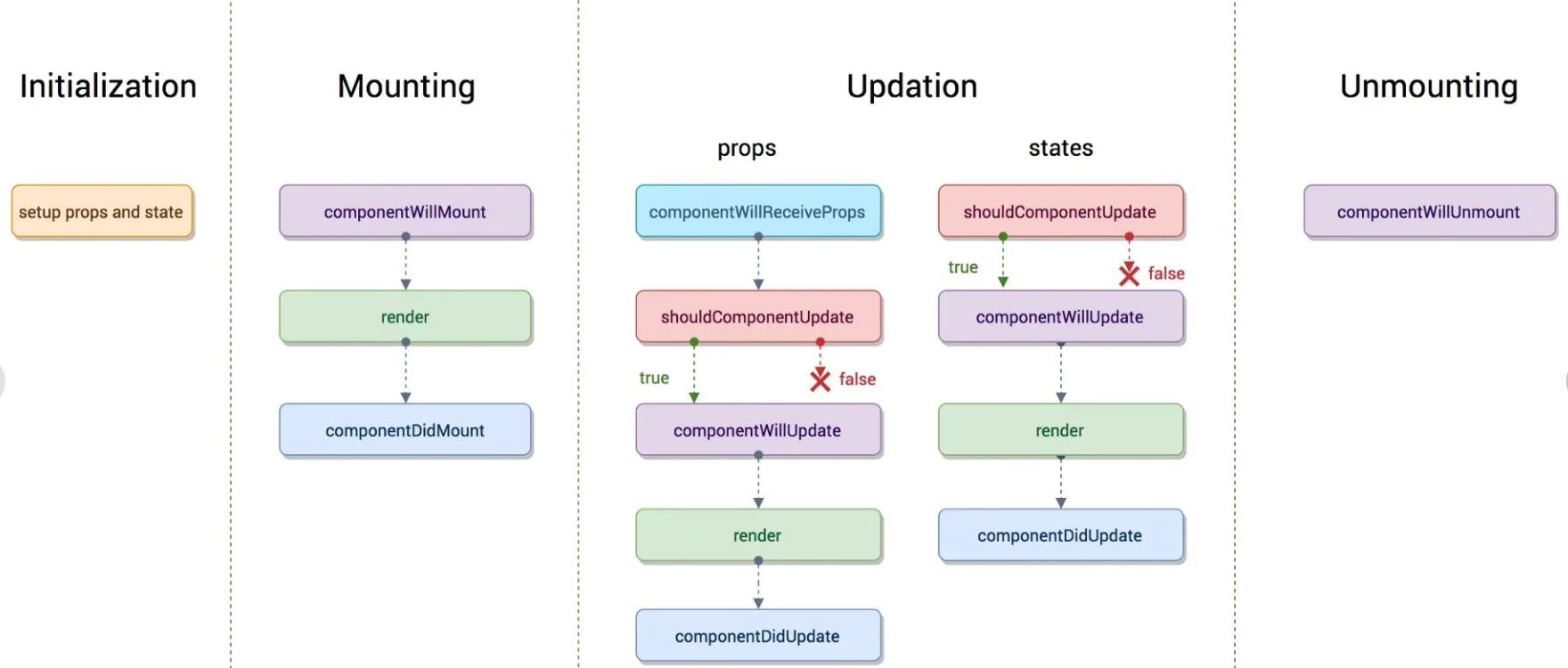
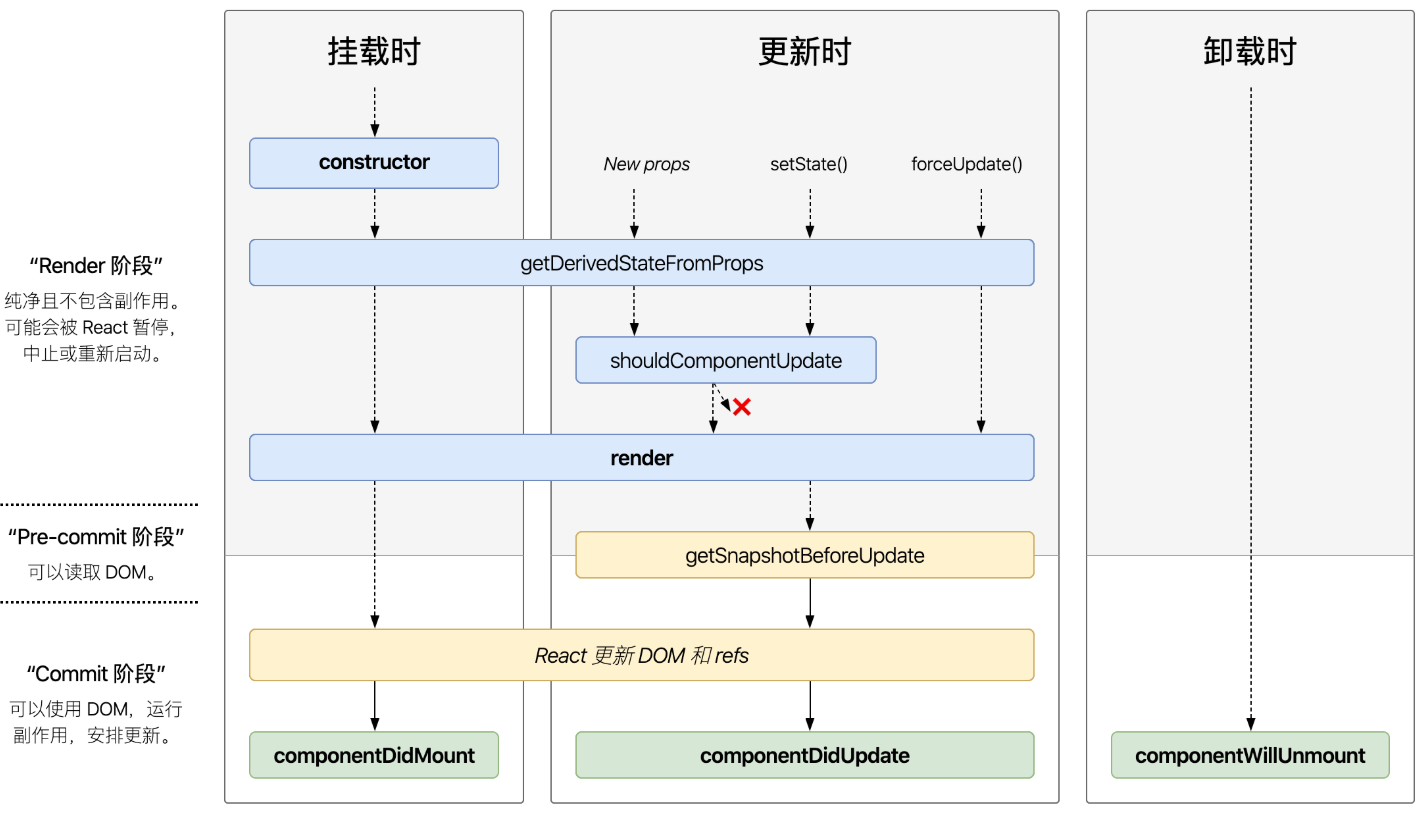
四、finishClassComponent
通过以上的情况执行后,会拿到 shouldUpdate 判断是否需要执行组件中的 render,并返回 render 下的第一个 child。
function finishClassComponent(...) {
...
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
let nextChildren;
...
nextChildren = instance.render();
...
if (current !== null && didCaptureError) {
//出错后 需要重新计算节点 mountChildFibers(初始) 后续 reconcileChildFibers
forceUnmountCurrentAndReconcile(...);
} else {
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
...
//返回下个节点,时间分片执行
return workInProgress.child;
}本篇对类组件的一些大概分析,下一篇开始进入 reconcileChildren 调和,又是一块硬骨头!
0人赞